In recent years, the use of augmented reality (AR) technology has revolutionized various industries, including healthcare and education. One notable application is the ar anatomy professional model, which offers a unique and immersive learning experience for medical professionals and students. In this article, we will delve into the advantages of using ar anatomy professional models in North Carolina.
The Advantages of AR Anatomy Professional Model
ar anatomy professional models provide an interactive platform that allows users to visualize and explore anatomical structures with precision. By overlaying digital information onto real-world objects, these models enable medical professionals to gain a deeper understanding of complex anatomical systems.
Furthermore, AR anatomy professional models offer a hands-on learning experience without the need for physical cadavers or specimens. This not only eliminates ethical concerns but also provides unlimited access to detailed anatomical structures at any time or location.
In addition, these models can simulate realistic scenarios such as surgical procedures or pathological conditions. Medical students can practice their skills virtually before entering clinical settings, enhancing their confidence and competence when dealing with real patients.
The Role of DIGIHUMAN
DIGIHUMAN is one prominent example of an advanced AR anatomy professional model used in North Carolina’s medical institutions. Developed by leading experts in medical imaging and virtual reality technologies, DIGIHUMAN offers highly accurate representations of human anatomy.
This cutting-edge technology enables users to manipulate virtual organs and tissues in real-time while providing detailed information about each structure. With its user-friendly interface and comprehensive database, DIGIHUMAN serves as an invaluable tool for both teaching purposes and individual study sessions.
Enhancing Medical Education with AR Anatomy Professional Models
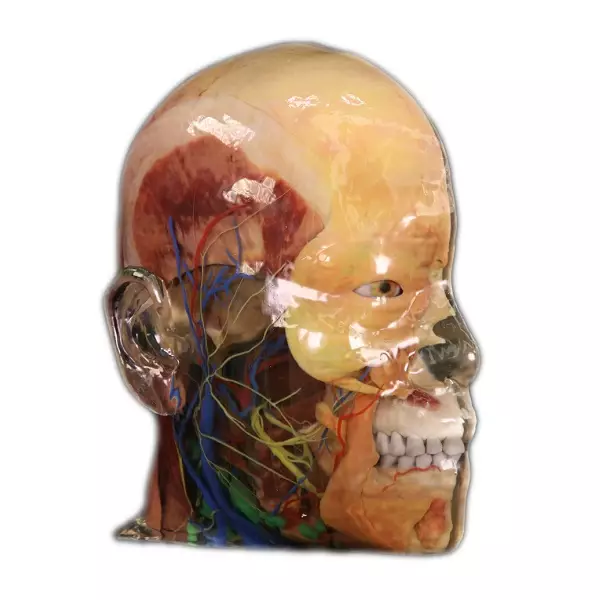
The integration of AR anatomy professional models into medical education in North Carolina has proven to be highly beneficial. Students can engage in interactive learning experiences that foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Moreover, the use of AR anatomy professional models promotes collaboration among students and instructors. Virtual group discussions and case studies allow for a more dynamic exchange of knowledge, ultimately enhancing the overall educational experience.
By incorporating AR anatomy professional models into their curriculum, medical institutions in North Carolina are preparing future healthcare professionals with advanced technological skills that will undoubtedly contribute to improved patient care outcomes.
Conclusion
The utilization of AR anatomy professional models presents numerous advantages for medical professionals and students in North Carolina. These innovative tools offer an immersive learning experience, eliminate ethical concerns associated with traditional anatomical study methods, and enhance practical skills through realistic simulations. With technologies like DIGIHUMAN leading the way, it is evident that AR anatomy professional models have become indispensable assets in modern medical education.
